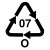
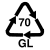
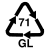
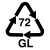
To make a correct separate collection, it is important to know the material from which the objects are made. Some are easily identifiable and we have no doubts about where to give them; others, such as polylaminates, always leave some doubts. For this reason, on the product packaging there are distinctive symbols that help us decipher the material from which they are formed and, therefore, the correct way in which to divide them.
The recycling symbols are international codes that uniquely identify the material from which an object is made and are a fundamental tool for citizens who want to understand how to make a perfect separate collection.

In the previous article we explained that packaging is recycled exclusively, or almost exclusively, or those products that have the function of protecting, containing and transporting the goods. This is already a good yardstick when we have to decide in which container to give a waste but, for the purpose of a correct and effective separate collection, it is important to also know the distinctive codes and symbols that uniquely identify a material.
When we talk about the recycling symbols we immediately think of those printed on the garbage cans but there are many other no less important codes that are found on the packaging and containers of the products we buy and which help us differentiate correctly.
The packaging, in fact, are often made with innovative or multi-coupled materials and can leave some doubts about their transfer. Here the symbols of the differentiated come into play, which exactly report the material of which an object is composed.
Below you will find a table realized by SmartRicicla with the most common identification symbols of the materials and their destination in the separate collection operations.
|
PLASTIC |
||
|
|
PET |
Polyethylene terephthalate or arnite: Bottles of water, bottles of drinks, bottles of shampoo |
|
|
PE-HD |
High density polyethylene: yogurt containers, detergent bottles |
|
|
PVC |
Polyvinyl chloride: Food containers |
|
|
PE-LD |
Low density polyethylene: Frozen food bags, squeezable bottles |
|
|
PP |
Polypropylene or Moplen: Ketchup bottles
|
|
|
PS |
Polystyrene or Polystyrene: Disposable glasses
|
|
|
O |
All other plastics |
|
METALS |
||
|
|
FE |
Steel – Iron |
|
|
ALU |
Aluminum |
|
TEXTILE |
||
|
|
TEX |
Cotton |
|
|
TEX |
Jute |
|
PAPER |
||
|
|
PAP |
Corrugated cardboard: Boxes containing furniture in kit |
|
|
PAP |
Non-corrugated cardboard: Packs of sandwiches in fast-food |
|
|
PAP |
Paper: Packaging of fries in fast-food, newspaper, paper bags |
|
GLASS |
||
|
|
GL |
Transparent / colorless glass: Bottles of water |
|
|
GL |
Glass of green color: Bottles of wine |
|
|
GL |
Glass of brown color: Bottles of beer |
|
WOOD |
||
|
|
FOR |
Wood |
|
|
FOR |
Cork |